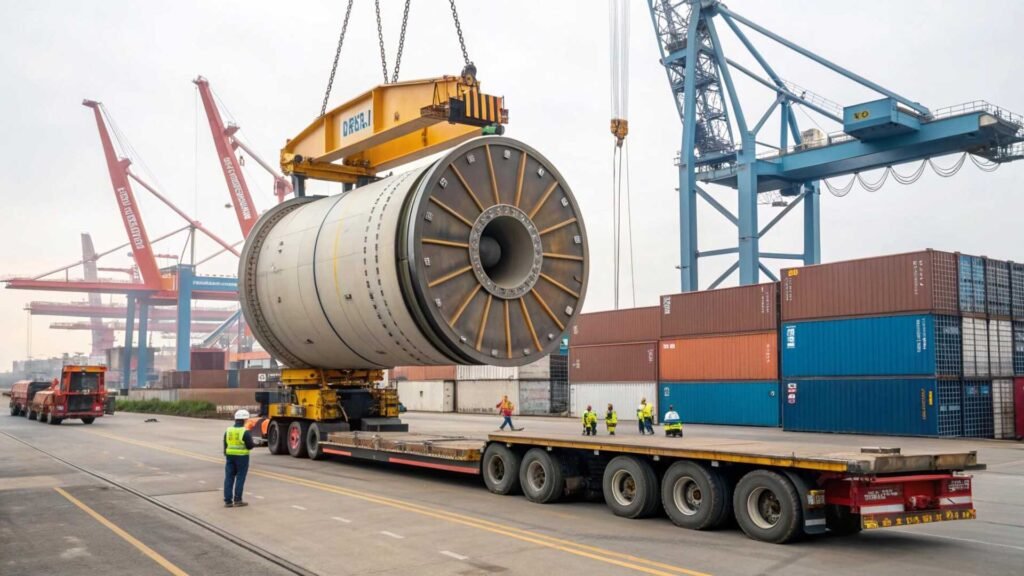
Feeling lost in the world of industrial logistics1? This complex process can be confusing, leading to expensive errors. Let's clarify what it means for your business's success.
Industrial logistics is the specialized management2 of the flow of heavy materials3, large machinery, and components within the industrial and manufacturing sectors. It differs from general logistics by handling oversized, heavy, or hazardous goods, requiring special equipment, planning, and coordination for production lines and large-scale projects.
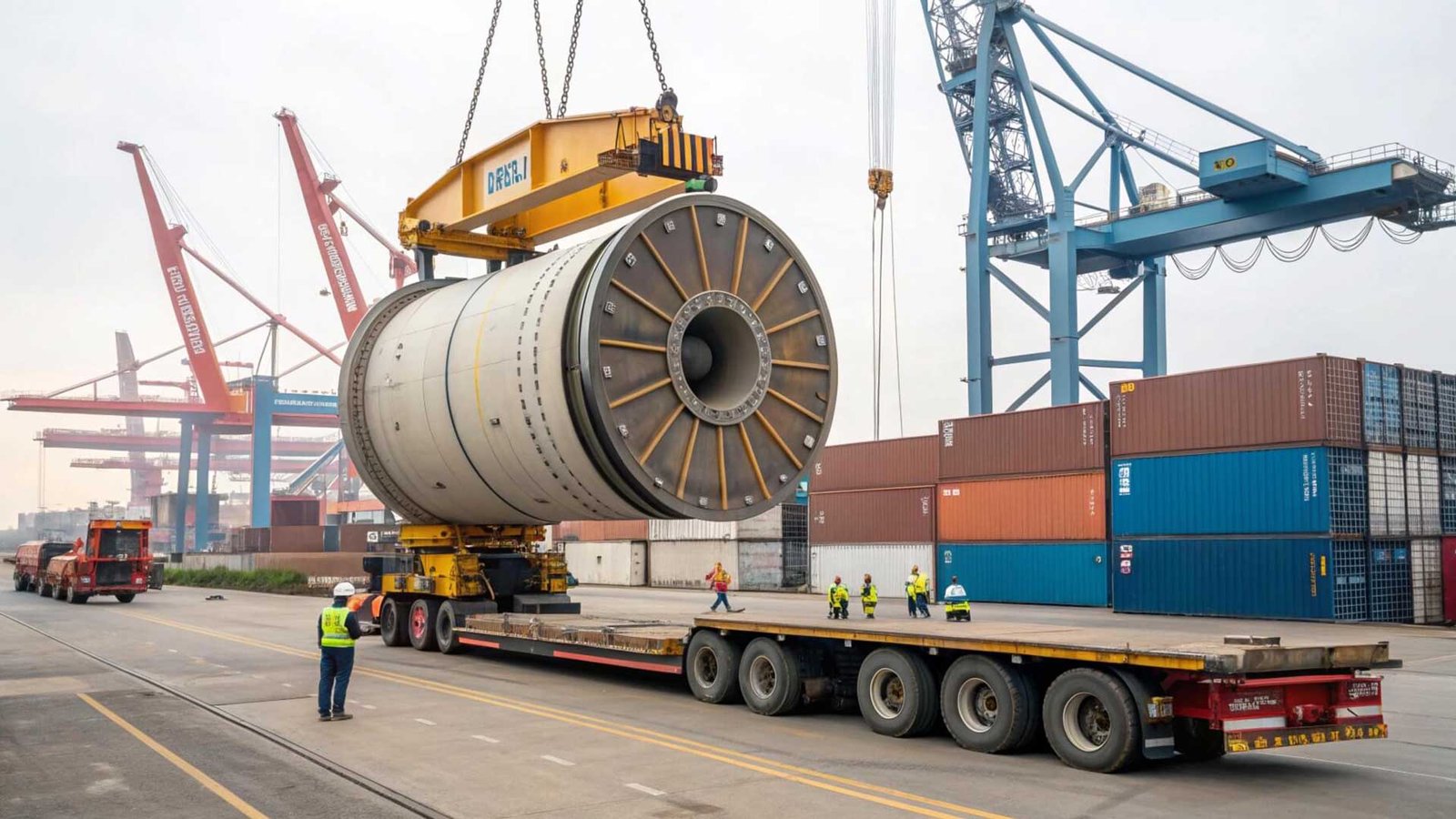

I remember talking to a client, Mark, who was struggling to get a large piece of equipment from China. He thought logistics was just another word for shipping. But it is so much more than that. He was detail-oriented and wanted to save costs, but the complexity of moving industrial goods was causing him headaches. Understanding the details is what separates a smooth project from a costly disaster. Let's dig into the specifics to give you a clearer picture.
What Is the Actual Work of Logistics?
Think logistics is just moving boxes? This oversimplification can cause major supply chain disruptions4. Let's look at the real, detailed work involved in successful logistics operations.
The work of logistics involves planning, implementing, and controlling the movement and storage of goods, services, and information. It covers everything from procurement and warehousing to transportation and final delivery, ensuring items get to the right place at the right time in the right condition.

Logistics is not a single action. It is a complete process. I see it as the central nervous system of a supply chain. It's about making sure everything works together smoothly. To understand it better, we can break the work down into three main areas.
Planning and Strategy
This is the first and most critical step. Before anything moves, we have to create a plan. This involves forecasting demand, choosing the right transportation modes5, and planning inventory levels. For a client like Mark importing from China, this means deciding if sea or air freight is better. It also means planning for potential delays, like customs inspections or bad weather. A good plan minimizes surprises and saves money.
Execution and Management
This is where the plan is put into action. It includes sourcing materials, managing warehouses, and coordinating transportation. For example, my team handles the execution of shipping containers from China to the USA. We book the vessel, manage the paperwork, and track the shipment. This stage is all about active management and problem-solving.
Control and Optimization
Logistics doesn't end when a shipment is sent. We must constantly monitor its progress. This involves tracking shipments, managing performance, and analyzing data. If a container is delayed, we need to know why and how to fix it. We use this information to optimize future shipments, making them faster and more cost-effective. It's a cycle fatores of continuous improvement.
What's the Difference Between Logistics, Freight, and Warehousing?
Are you using "freight" and "logistics" interchangeably? This common confusion can lead to miscommunication with partners. Let's define these key terms to make you a smarter shipper.
Logistics is the overall strategic process of managing how resources are acquired, stored, and transported. Freight is the goods being shipped, and freighting is the act of transport. Warehousing is just one component of logistics, focusing on a product's storage and handling.

Many of my clients initially get these terms mixed up. It's an easy mistake to make. But knowing the difference is important when you are planning your supply chain. It helps you ask the right questions and hire the right services. Think of it like building a house. Logistics is the architect's overall blueprint. Freight is the building materials, and warehousing is the storage shed where you keep them.
Here is a simple table to show the differences:
| Term | Scope | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Logistics | Broad (Strategic) | Overall planning, execution, and control of the supply chain. |
| Freight | Narrow (Physical) | The goods themselves or the act of transporting them. |
| Warehousing | Specific (Component) | Storing, managing, and preparing goods for shipment. |
Logistics is the big picture. It's the strategy that connects everything. When you hire my company for DDP shipping, you are hiring us for our logistics expertise. We plan the entire journey.
Freight is the physical part. It's the actual container of goods you are shipping. The term "freight" can refer to the cargo or the money you pay to ship it.
Warehousing is a single, important piece of the logistics puzzle. It's where your goods are stored before, during, or after transport. A warehouse isn't just for storage. It's also where goods are sorted, packed, and prepared for the next step.
What Are the Main Types of Logistics?
Does your logistics strategy cover everything? Many businesses focus only on shipping, ignoring other crucial types. This oversight can create hidden inefficiencies and costs in your supply chain.
The main types of logistics include inbound (managing incoming supplies), outbound (delivering to customers), reverse (handling returns), and third-party logistics (3PL, outsourcing). Each type addresses a different stage of the supply chain, from raw materials to a finished product's return.
Thinking about logistics in different categories helps you organize your operations. Each type has its own challenges and requires a specific focus. As a logistics provider, I deal with these different types every day. Let's break them down.
Inbound Logistics
This is all about getting things into your business. It involves the sourcing, ordering, and transportation of raw materials or goods from your supplier to your facility. If you are a manufacturer in the US, your inbound logistics6 could be managing the shipment of parts from a factory in China. The goal is to get what you need efficiently to keep production running.
Outbound Logistics
This is the opposite. It's about getting finished products out to your customers. This includes storing the finished goods, processing orders, and arranging delivery. For an online seller, outbound logistics7 is everything that happens after a customer clicks "buy". The goal is customer satisfaction through timely and accurate delivery.
Reverse Logistics
This flusso is often overlooked but is very important. Reverse logistics deals with the return of goods from the customer back to the seller. This could be for returns, repairs, or recycling. It requires its own process for receiving, inspecting, and restocking or disposing of the items. A good reverse logistics8 plan can save money and improve customer loyalty.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
This is when a company outsources its logistics operations to a specialized provider, like my company. A 3PL provider can handle inbound, outbound, and even reverse logistics8. Businesses do this to save money, gain expertise, and focus on their core product or service.
Why Is Logistics So Necessary in the Industrial Sector?
Think you can manage industrial projects without a solid logistics plan? This is a recipe for disaster. Let's explore why logistics is the backbone of any successful industrial operation.
Logistics is vital in the industrial sector to ensure a seamless flow of raw materials, heavy machinery, and finished goods. It prevents production delays, manages complex supply chains, reduces operational costs, and ensures safety when handling oversized or hazardous materials, directly impacting project timelines and profitability.

Industrial logistics is a different beast. We are not just talking about standard boxes. We are talking about multi-ton machinery, long steel beams, or hazardous chemicals. I once helped a client who was building a new factory. His main processing machine was stuck at the port in Los Angeles. The paperwork was incorrect for such a large, specialized item. We helped him get it cleared, but the one-week delay cost him tens of thousands of dollars in lost production time. This is why specialized industrial logistics1 is not a luxury. It is a necessity.
Keeping Production Lines Running
Industrial manufacturing relies on a concept called "just-in-time9". This means raw materials arrive just as they are needed for production. This minimizes storage costs. But it requires perfect logistics. A single delayed shipment can shut down an entire assembly line.
Managing Oversized and Heavy Cargo
Moving a 50-ton generator is not like shipping a pallet of T-shirts. It requires special permits, special trucks or ships, and expert planning. Industrial logistics specialists know how to handle these challenges safely and legally.
Cost and Time Efficiency
A good logistics plan finds the most efficient route and transport mode. This saves money on fuel and transport costs. It also ensures projects finish on time. In the industrial world, time मशीन is money. Delays can lead to huge financial penalties. Proper logistics planning directly protects your bottom line.
What Are the Main Transportation Modes in Industrial Logistics?
Choosing the wrong transport mode? This can inflate costs and cause massive delays. Let's review the main options to help you make a smarter, more cost-effective choice.
The main modes are sea, air, road, and rail. Sea freight is best for large, non-urgent volume. Air is for fast, high-value cargo. Road offers door-to-door flexibility. Rail is great for heavy, long-distance inland transport. The choice depends on cost, speed, and cargo type.
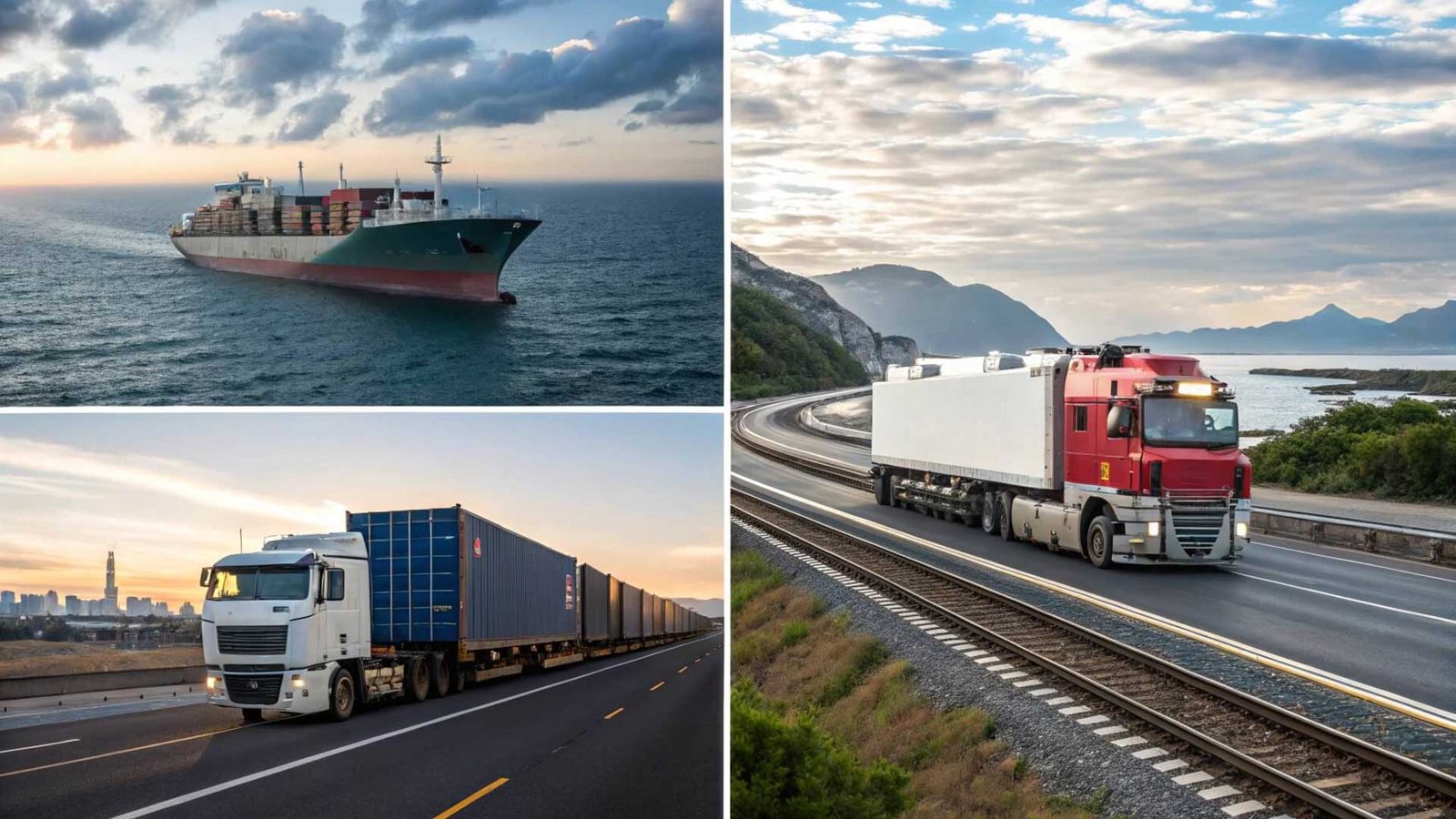

Choosing the right transportation mode is a core part of logistics strategy. For my clients shipping from China to the US, this is one of the first questions we answer. The best choice is a balance of speed, cost, and the type of cargo. There is no single "best" mode. It always depends on the situation.
Here’s a breakdown to help you compare:
| Mode | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea/Ocean | Large volume, low cost, oversized cargo | Cheapest per unit, high capacity | Slowest, port-to-port only |
| Air | Speed, high-value goods | Fastest transit time | Most expensive, size/weight limits |
| Road (Truck) | Flexibility, last-mile delivery | Door-to-door service, highly flexible | Slower than air, traffic delays |
| Rail | Heavy inland cargo, long distance | Cost-effective for bulk, reliable | Limited network, less flexible |
Often, the best solution is a mix of these modes. This is called intermodal transportation10. For example, a container might travel by ship from Shanghai to a US port. Then it is loaded onto a train to travel inland to a city like Chicago. Finally, a truck takes it from the rail yard to the final destination. My job is to coordinate all these steps to create one smooth journey. For industrial goods, sea and rail are very common due to their ability to handle heavy and bulky items cost-effectively.
How Can Logistics Become More Sustainable?
Worried about your company's carbon footprint? Logistics is a major contributor to emissions. Let's explore practical ways to make your supply chain greener and more efficient.
Logistics can become more sustainable by optimizing routes to reduce fuel consumption, using electric or alternative-fuel vehicles, consolidating shipments to maximize space, and adopting green warehousing practices like using solar power and reducing waste. It's about efficiency and environmental responsibility.

Sustainability is becoming more important to my clients. They want to be responsible, and they also know that efficiency 오래 often means being greener. A green supply chain is not just good for the planet. It can also be good for your profits. Wasted fuel is wasted money. An empty truck is a missed opportunity. Here are some practical ways we can make logistics more sustainable.
Route and Load Optimization
This is the easiest win. Using smart software, we can plan the shortest and most efficient routes for trucks. We can also consolidate shipments. This means we wait until a truck or container is full before sending it. This drastically reduces the number of trips, saving fuel and reducing emissions.
Green Transportation
The vehicles themselves are changing. Electric and hydrogen-powered trucks are becoming more common for road transport. For sea freight, shipping lines are investing in more fuel-efficient vessels and exploring alternative fuels like LNG or ammonia. Choosing sea freight over air freight is a major sustainability choice, as air travel has a much larger carbon footprint.
Sustainable Warehousing
Warehouses can also be made greener. This includes simple things like using LED lighting and better insulation. It can also involve bigger steps, like installing solar panels on the roof to generate clean energy. Reducing packaging waste and using recyclable materials also makes a big difference.
A focus on sustainability is now a key part of modern logistics. It's about being smarter, more efficient, and more responsible.
What Are the Real Differences Between Inbound and Outbound Logistics?
Are you treating your incoming supplies and outgoing products the same way? This can cause major bottlenecks. Let's clarify the key differences to streamline your entire operation.
Inbound logistics is about bringing supplies or raw materials into your business from suppliers. Outbound logistics is about moving finished goods out of your business to the end customer. Inbound focuses on sourcing and storage, while outbound focuses on delivery and customer service.
Understanding the distinction between inbound and outbound logistics is crucial for managing your supply chain effectively. They are two sides of the same coin, but they require different strategies and have different goals. I help clients manage their inbound logistics from China. This means I'm focused on getting their goods to them reliably and on time so they can run their business.
Here is a table that clearly lays out the differences:
| Feature | Inbound Logistics | Outbound Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Sourcing and receiving materials | Delivering products to customers |
| Key Parties | Supplier → Your Company | Your Company → Customer |
| Main Goal | Supply production efficiently | Fulfill customer orders |
| Activities | Procurement, receiving, storing | Order processing, packing, shipping |
For inbound, the main challenge is managing relationships with many suppliers. You might be sourcing parts from ten different factories. The goal is to coordinate all these shipments to arrive when you need them, without building up too much expensive inventory.
For outbound, the main challenge is meeting customer expectations. Customers today want fast, reliable, and often free shipping. The goal is to manage a distribution network that can deliver products to thousands of individual customers quickly and accurately.
While they are different, they are deeply connected. A delay in your inbound logistics (a part doesn't arrive from China) will directly cause a delay in your outbound logistics (you can't ship the finished product to your customer). A well-run company needs to master both.
Conclusion
Industrial logistics is more than just moving goods. It's the strategic core of your operation. Understanding its parts helps you build a more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable supply chain.
Understanding industrial logistics is crucial for managing the flow of heavy materials and machinery, ensuring efficiency and safety in large-scale projects. ↩
Specialized management in logistics ensures the safe and efficient handling of oversized, heavy, or hazardous goods, crucial for industrial success. ↩
Managing the flow of heavy materials is essential to prevent costly errors and ensure smooth operations in industrial logistics. ↩
Preventing supply chain disruptions through effective logistics is vital for maintaining smooth operations and avoiding costly delays. ↩
Choosing the right transportation mode in logistics affects cost, speed, and efficiency, crucial for successful delivery. ↩
Inbound logistics is crucial for sourcing and transporting raw materials efficiently, ensuring smooth production processes. ↩
Outbound logistics focuses on delivering finished products to customers, directly impacting customer satisfaction and business success. ↩
Reverse logistics handles returns and recycling, improving customer loyalty and reducing costs through efficient management. ↩
Just-in-time logistics minimizes storage costs by ensuring materials arrive exactly when needed, crucial for efficient production. ↩
Intermodal transportation combines multiple modes for efficient delivery, optimizing cost and speed in logistics. ↩




